

For example, the notes of the F natural minor scale are F – G – A♭- B♭- C – D♭- E♭- F. The harmonic minor scale raises the seventh note of the natural minor scale by a half-step, when ascending and descending the scale. Let’s now take a look at the F harmonic minor scale. Its notes are Eb – G – Bb.Ĭhords in the key of F minor. Let’s now take a look at the chords in the key of F minor. Thumb: 1, index finger: 2, middle finger: 3, ring finger: 4 and pinky finger: 5. What are the fingerings for the F minor scale? They are as follows: Finally, we move a whole step from Eb to F. From Db, we move up one whole step to Eb. Next, we move a whole step from Ab to Bb. Let’s start on F and move a whole step to G. (A whole step skips a key while a half step moves to the next key.) Let’s try this with the F minor scale. You can memorize this formula to form any natural minor scale: whole step – half step – whole step – whole step – half step – whole step – whole step or w – h – w – w – h – w – w. The sixth note of a major scale becomes the root note of its relative minor. The difference is the root note of the two scales. For the Ab major scale, it’s A♭, B♭, C, D♭, E♭, F and G. The notes of the F minor scale as we’ve seen are F, G, A♭, B♭, C, D♭, and E♭. Minor keys and their relative major make use of the same notes. The relative major of F minor is Ab major. Here’s the F natural minor scale on piano. Here’s the F natural minor scale on the bass clef. Here’s a diagram of the F natural minor scale on the treble clef. Perfect 8th: F (one octave higher) is the 8th note of the B natural minor scale.Minor 7th: Eb is the 7th note of the scale.Minor 6th: Db is the 6th note of the scale.Perfect 5th: C is the 5th note of the scale.Perfect 4th: Bb is the 4th note of the scale.Minor 3rd: Ab is the 3rd note of the scale.Major 2nd: G is the 2nd note of the scale.Tonic: F is the 1st note of the F natural minor scale.To learn more about this scale and others, check out my course, Learn Scales & Music Theory & Give Yourself An Upper Hand. This scale consists of the pitches, F, G, A♭, B♭, C, D♭, and E♭. Let’s start with the F natural minor scale. We will take a look at the three types of minor scale, the natural minor, melodic minor and harmonic minor scales. This unique interval structure is what determines the flavor and mood of the scale.This lesson is all about the F minor scale. Just like all other musical scales, we use both a scale degree formula and semitone and tone interval formula (half and whole steps) to describe the melodic minor scale. Let's look at the notes in the key of C melodic minor as an example:Īscending = C - D - Eb - F - G - A - B - (C)ĭescending = C - D - Eb - F - G - Ab - Bb - (C) It is therefore played the same forwards and backwards. Played forwards, you play with a flat third and coming back down, you play the natural minor scale intervals we'll have a look at further down.Īs we've touched up, today in contemporary music, the melodic minor scale is liberally used in jazz, and within this context most jazz guitarists think of it as being the major scale with a flat 3rd. Taken in the traditional classical sense, the bizarre thing about the melodic minor scale is it is played differently ascending and descending. The Melodic Minor Scale Is Different Forwards & Backwards From jazz to folk to bebop, the melodic minor scale has a few extra quirks we're about to discover.

This split personality is what makes the melodic minor scale so useful for any guitar player wanting to expand their improvisation and writing horizons. (Minor tetrachord) C - D - Eb - F G - A - B - C (Major tetrachord) Taking the C melodic minor scale as an example, here are its two opposing halves: Major tetrachord = Tone - Tone - Semitone Minor tetrachord = Tone - Semitone - Tone The first half, with it's minor third interval has a minor flavour, whilst the top half sounds major.įor this reason, the scale can be thought of as two tetrachords (a 4 note chord spread over 5 semitones within a perfect 4th interval) separated by one whole tone: Owing to its interval structure, the melodic minor scale can't quite make up its mind up if it's major or minor. This versatile scale is popular with jazz guitar players and because of this is sometimes referred to as the "jazz minor scale". It is a 7 note scale with a flat 3rd separating it from its happy sounding major counterpart.
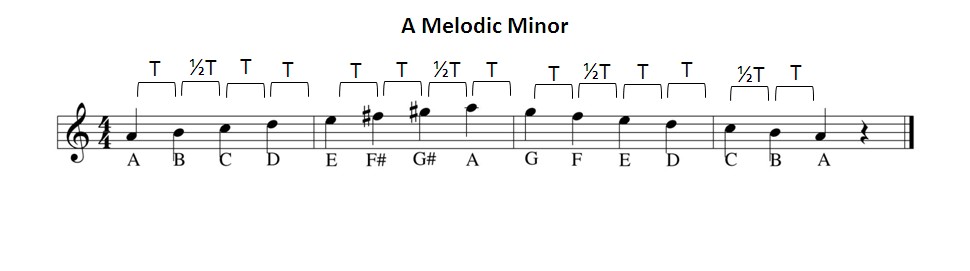
The melodic minor scale, despite its name, is almost identical to the major scale. What Is The Melodic Minor Scale on Guitar?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
